How does a vape produce vapor?

Vaping means breathing in vapor produced by an electronic device. People often use it instead of smoking. A vape has important parts: the battery, heating element, and e-liquid. Each part is crucial for how vapes produce vapor. Understanding these components helps you make informed choices about vaping.
Key Takeaways
A vape makes vapor by using a battery. The battery powers a coil that heats e-liquid. This turns the e-liquid into vapor you can breathe in.
Different types of coils and e-liquid mixes change the flavor, vapor size, and throat hit. This lets you make your vaping experience unique.
Keeping your battery charged is important. Choosing the right coil and controlling the temperature help make vaping safe and fun.
Battery Function

Powering the Coil
The battery is very important for your vape device. It gives power to the coil, which heats the e-liquid. When you turn on the device, the battery sends electricity to the coil. This makes the coil heat up fast and change the liquid into vapor.
Tip: Always keep your battery charged for a good vaping experience.
Battery Types
Vape devices usually have two main battery types: internal (built-in) and external (removable).
Internal (Built-in) Batteries
These are often lithium polymer batteries inside the device.
Advantages:
Made with safety features by the maker.
Need less care from you.
Disadvantages:
Have a short life and can't be changed.
You must get a new device when the battery stops working.
External (Removable) Batteries
These are usually lithium-ion batteries like 18650, 20700, and 21700.
Advantages:
Easy to change and recharge separately.
Let you customize and use more power.
Make the device last longer since you can swap out dead batteries.
Disadvantages:
Need extra safety knowledge.
Can be bigger and harder to carry.
Knowing these battery types helps you pick the right vape device for you. Always focus on safety by using trusted brands and checking your batteries often.
Heating Element and Vapor Production
The heating element, also known as the atomizer, is very important for how your vape makes vapor. It has a coil that heats up when the battery powers it. This heating changes the e-liquid into vapor, which you can inhale.
Coil Types
Different coils change how much vapor you get and the flavor. Here are some common coil types you might see:
Sub-ohm Coils: These coils have a resistance below 1.0 ohm. They create big vapor clouds and strong flavor because of their low resistance. But, they use more battery power.
Mouth-to-Lung (MTL) Coils: These coils have tighter airflow, which means less vapor. They give a richer, stronger flavor, similar to traditional smoking.
Temperature Control Coils: These let you set exact temperatures. This helps prevent dry hits and keeps the flavor steady.
Rebuildable Dripping Atomizer (RDA) and Rebuildable Tank Atomizer (RTA) Coils: These allow you to customize by building your coils, which affects flavor and cloud size.
Ceramic Coils: Known for their smooth, clean flavor, ceramic coils also last longer than regular coils.
The materials used for coils are important too. Common materials are Kanthal, stainless steel, nickel, and titanium. Each material has special heating properties that affect how well it heats and the flavor quality.
Heating Process
When you turn on your vape, the battery sends electricity to the coil. This electricity meets resistance, creating heat through a process called resistance heating or the Joule effect. The coil heats up quickly and transfers heat to the wick, which soaks up the e-liquid. As the wick gets warm, it turns the liquid into vapor, which you inhale.
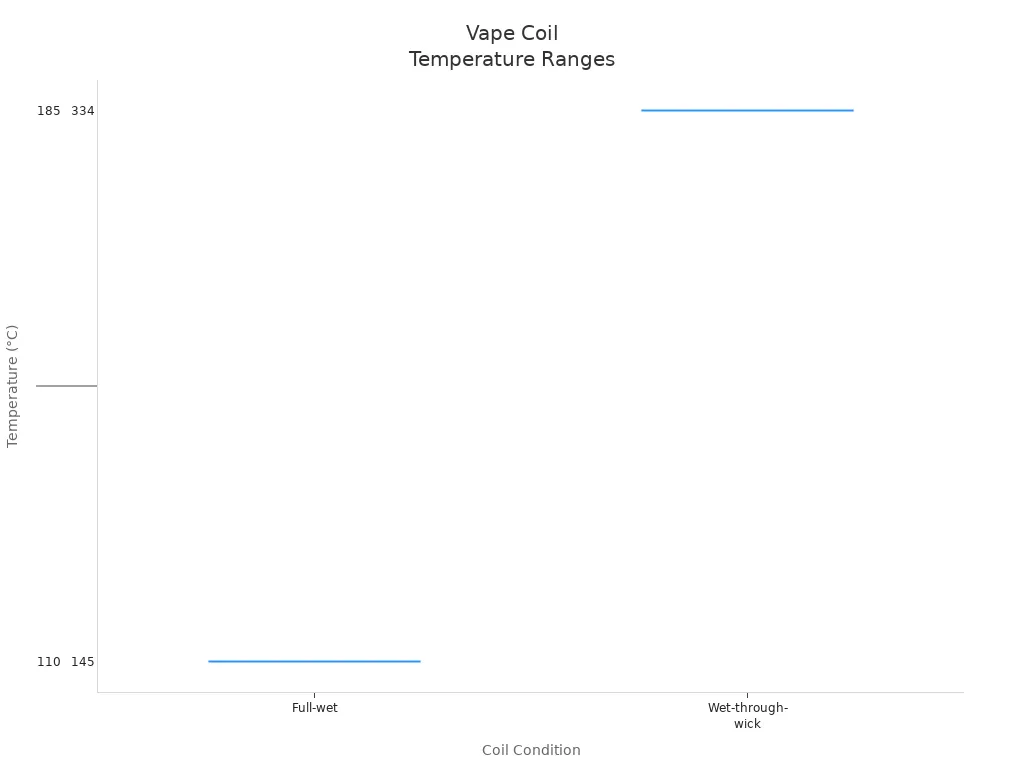
The coil's temperature can change while it works. Usually, the coil gets between 110°C and 334°C, depending on the situation. For example, when the coil is wet, it stays below the boiling point of propylene glycol (PG), which is about 188°C. But if the coil runs dry, it can get much hotter, causing a bad taste called a "dry puff."
The coil's resistance greatly affects how much and how good the vapor is. Lower resistance coils heat up faster, making bigger vapor clouds and stronger flavors. On the other hand, higher resistance coils heat up slower, giving softer vapor with smaller clouds. Choosing the right coil resistance depends on how you like to vape and what kind of vapor you want.
Knowing how the heating element works helps you understand how your vape makes vapor. By picking the right coil type and resistance, you can improve your vaping experience.
How Vapes Produce Vapor
E-liquid Composition
E-liquids are very important for vaping. They have several main parts that help make vapor. The main ingredients are:
Propylene Glycol (PG): This liquid carries flavor and gives a throat hit like smoking.
Vegetable Glycerin (VG): VG is thicker and sweeter than PG. It makes bigger vapor clouds but can feel smoother in your throat.
Flavorings: These are strong substances that add taste to the vapor. They can be fruity or dessert-like.
Nicotine: This is an addictive chemical that comes in different strengths. It changes how you feel and the vapor's makeup.
The mix of PG and VG affects the vapor you breathe in. A higher PG amount (like 70/30) gives a stronger throat hit. A higher VG amount (like 70/30) makes thicker vapor clouds. This mix lets you change your vaping experience to what you like.
The way e-liquid turns into vapor has several steps:
The battery powers the atomizer coil.
The wick soaks up e-liquid from the tank or pod.
The coil heats the e-liquid in the wick, turning it into vapor.
After making vapor, the wick soaks up more e-liquid for the next puff.
Modern mesh coils heat up quickly, making vaporization faster and better. This teamwork between the wick, coil, and e-liquid helps you get a good puff every time.
Temperature Effects
Temperature is very important for making vapor. The coil's heat affects how much vapor is made and how good it is. Here are some key points to think about:
Low Temperatures (200°F–350°F): These temperatures make flavors clearer, creating thinner vapor and a softer throat hit.
Medium Temperatures (350°F–400°F): This range balances flavor and vapor, making denser clouds and a moderate throat hit.
High Temperatures (400°F–600°F): These temperatures increase vapor and throat hit but can also burn flavors and damage coils.
Temperature control in modern devices helps stop overheating. They turn off power when a set temperature is reached, preventing dry hits and burnt coils. This keeps your vaping experience tasty and safe.
However, overheating can create harmful byproducts. At normal vaping temperatures below the boiling point of glycerol (~288 °C), e-liquids mostly vaporize without burning. But as temperatures go up, harmful compounds like formaldehyde and acetaldehyde can increase, especially near or above 266 °C. These compounds can be bad for your health, so it's important to keep good temperatures while using your vape.
In short, you found out that a vape makes vapor using three main parts: the battery, heating element, and e-liquid. The battery gives power to the coil. This coil heats the e-liquid and turns it into vapor. Knowing how this works helps you pick the right vape device. Think about things like the type of device, airflow control, and coil compatibility to improve your vaping experience.
Tip: Always pick trusted brands and focus on safety when vaping.
FAQ
What is the difference between PG and VG in e-liquids?
PG gives a throat hit and carries flavor. VG makes thicker vapor clouds and feels smoother.
How often should I change my vape coil?
Change your coil every 1-2 weeks. This depends on how much you use it and the flavor quality.
Can vaping help me quit smoking?
Vaping might help you smoke less. Talk to a healthcare professional for advice and support.
